Introduction
Given no prior knowledge of jet pumps and their performance, we must take a hypothetical situation and understand how to apply this information to it. The situation we decided to determine is how long it would take to evacuate a room with gaseous byproducts due to fermentation. We assume this room is of size 5000 gallons, and the suction pressure is at 90%. Now, this analysis requires an in-depth understanding of how jet pumps work and how they are applied. Below is a brief diagram of how these work. Simply they use a pre-existing technology in the venturi tube in order to apply this principle. These devices when applied to jet pumps are referred to as eductors.
Figure 1. Schematic of the eductor used in the experiment. Motive fluid enters and creates friction from the inlet gas resulting in a much higher rate of velocity through the venturi. The venturi creates a zero pressure environment that allows for it to push the motive fluid at a much higher velocity. These types of eductors are incredibly useful for the application covered in our hypothetical.
Performance
Initially, in order to determine the performance and how both independent variables being the suction valve and control valve, impact the flow rate of the jet pump. Below is a slightly messy chart that attempts to display all data collected.
Figure 3. Comparison of flow rates for every suction percentage and control valve pressure explored in the experiment. Each data point for each suction level is the average of 6 different readings gathered. This allows for a better interpretation of the data and helps to mitigate errors through calculation.
Solving the Hypothetical
In order to solve this problem, there needed to be a way of understanding the goals of what we are attempting to achieve. To begin with, we need to find the cost and time required with this situation applied. The only number we need to calculate is the flow rate at the given conditions. We assume the control valve is open fully to ensure the maximum flow rate. In order to calculate the coefficient of drag, since it is a large equation EES was needed to solve.
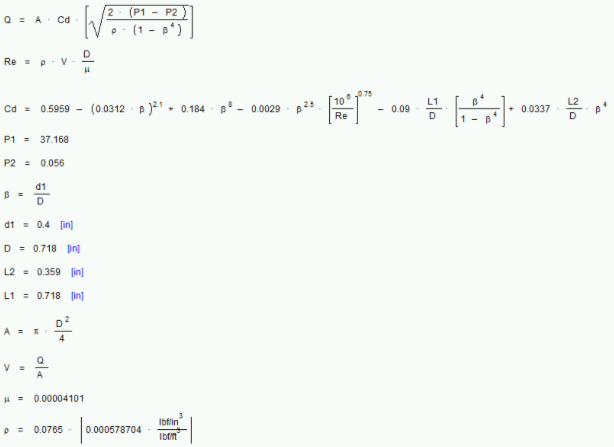
After finding the flow rate at maximum motive fluid and with suction of 90%, we are then able to determine the cost and time required to evacuate the room. The cost of electricity per kW-hr was calculated based on average Whitman County electricity costs.
time = (room volume)(flow rate)=(5000 gallons)/(1.311 gallons/sec)=63 min 32 sec
Cost = (0.0957$kW-hr)*(193.47kW)*(1.059hr)=$19.61
